Table of Contents
Guidance on Review Types
Whilst Nested Knowledge started out as a comprehensive tool for conducting systematic literature reviews, the software has grown into a dynamic environment for synthesizing diverse research methodologies. Our goal is to empower researchers to navigate the intricate landscape of evidence synthesis with ease, regardless of review type.
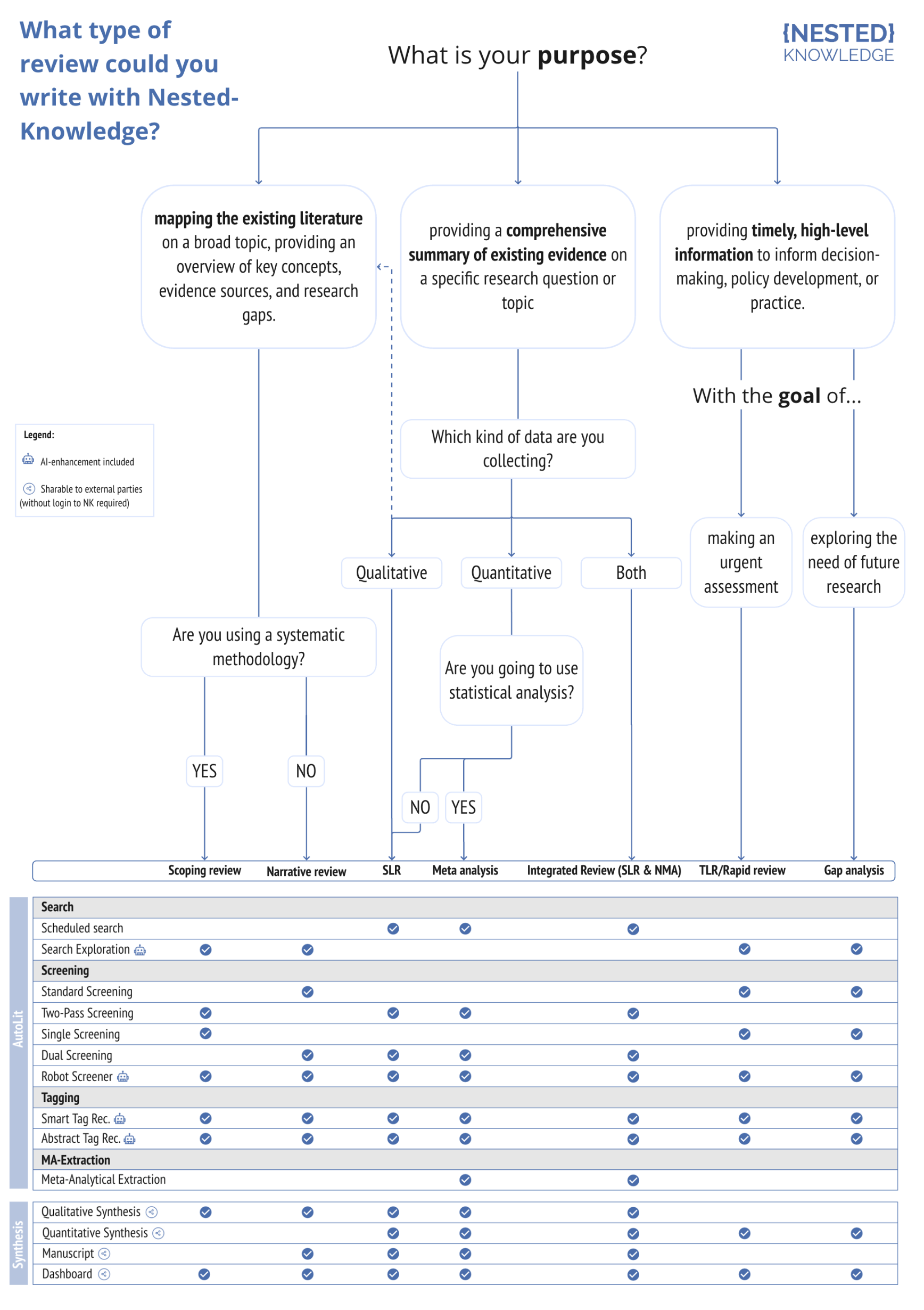
This page defines and discusses the typical review types conducted in Nested Knowledge, highlighting examples of specific nests conducted in the software previously. And, if you don't have a review type in mind, hopefully this will help guide you into making that decision before diving into your nest!
Note: only licensed users will be able to view beyond Synthesis (Outputs) of these nests.
Systematic Literature Review (SLR)
The first review type we have to mention is the glorious SLR. A comprehensive and methodical approach, SLRs systematically gather, appraise, and synthesize existing literature to answer specific research questions. Nested Knowledge provides a structured framework to facilitate the rigorous process of SLRs, ensuring clarity and transparency in evidence synthesis. See our Systematic Review Guide for more info.
Suggested Nest Setup:
- Librarian-assisted search query built for Literature Search
- Run automatic search on a schedule for a living SLR
- Toggle on Dual Two-Pass Screening mode in Settings
- Turn on Robot Screener in Settings when recall reaches appropriate threshold
- Set up Tag Hierarchy with pre-determined PICOs
- Turn on Smart Tag Recommendations for assistance in Tagging/evidence collection
- Use a Critical Appraisal system to assess Risk of Bias
- Download Exports: Tags in Study Inspector
- Assess and present evidence in Qualitative Synthesis
View an example of a published SLR in Nested Knowledge.
Meta-analysis (including Network Meta-analysis)
A meta-analysis uses statistical methods to summarize the results of a systematic review. After completing your systematic review in Nested Knowledge, you can utilize Meta-Analytical Extraction to pool quantitative data from multiple studies to derive meaningful insights. In the process, the software's capabilities extend to Network Meta-analysis, as Quantitative Synthesis is automatically generated. This interactive output enables a sophisticated examination of treatment comparisons within a broader network of evidence. See out Meta-analysis Guide for more info.
Suggested Nest Setup:
- Follow above steps to build an SLR
- After completing Tagging, toggle on Meta-Analytical Extraction in Settings
- Configure Interventions and Data Elements
- Complete MA Extraction to generate Quantitative Synthesis
- Download Exports: Meta-Analytical Extracted Data in Study Inspector
- Assess and present evidence in Quantitative Synthesis for NMA outputs
View an example of a published SLR & NMA in Nested Knowledge.
HTA Submissions
Nested Knowledge supports the Health Technology Assessment (HTA) process, largely catering to the clinical, epidemiological, and economic evaluation/cost-effectiveness aspects of submissions. Researchers can navigate these intricate components with ease, ensuring a comprehensive and well-rounded evaluation of healthcare technologies.
Clinical Effectiveness: This part of the HTA submission focuses on the clinical efficacy and safety of the health technology.
View an example of Clinical Effectiveness HTA assessment in Nested Knowledge.
Epidemiology: This part of the HTA submission addresses the broader population-level impact of the health technology, exploring the prevalence and incidence of the health condition targeted by the technology.
View an example of Epidemiological HTA assessment in Nested Knowledge.
Economic evaluation/Cost-effectiveness: This part of the HTA submission evaluates the economic aspects of the health technology, including considerations of direct costs, indirect costs, quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), and other economic metrics.
Suggested Nest Setup:
- Topic-assisted search queries should be built for Literature Search
- Toggle on Dual Two-Pass Screening mode in Settings
- Set up Tag Hierarchy with pre-determined PICOs regardless of review type
- Clinical reviews may involve MA Extraction and NMA, but Epidemiology and Cost-effectiveness reviews only involve Tagging
- Turn on Smart Tag Recommendations for assistance in Tagging/evidence collection
- Use a Critical Appraisal system to assess Risk of Bias
- Download Exports/Spreadsheets in Study Inspector
- Assess and present evidence in Synthesis outputs
View an example of incorporating Economic Evaluations as part of an HTA assessment in Nested Knowledge.
Targeted Literature Reviews/Rapid Review
When time is of the essence, Nested Knowledge facilitates targeted literature reviews and rapid reviews. Efficient and streamlined, this feature is ideal for quickly synthesizing relevant evidence to inform time-sensitive decisions and interventions.
Suggested Nest Setup:
- Rapidly check the PICOs of the search and build out strategy in Search Exploration,
- Toggle Standard, Single Screening mode in Settings
- Turn on Automatic Training of the Screening model in Settings, which will activate once 50 records are screened
- Apply a bulk action including records above assigned threshold and excluding below assigned threshold
- Configure Tag Hierarchy with only specific set of questions
- Turn on Abstract or Full Text Smart Tag Recommendations
- Apply a bulk action of accepting all tag recommendations to create preliminary, non-quality-controlled outputs
- If necessary, use a Critical Appraisal system to assess Risk of Bias
- Download Exports/Spreadsheets in Study Inspector
- Assess and present evidence in Synthesis outputs
View an example of a TLR/Rapid Review in Nested Knowledge.
Scoping Review
For researchers aiming to map the landscape of existing literature on a particular topic, Nested Knowledge provides tools for conducting scoping reviews. This approach helps define the breadth and depth of available evidence, setting the stage for more focused investigations.
Suggested Nest Setup:
- Enter broad PICO terms and build out initial search query in Search Exploration
- Set searches to run on a schedule to ensure comprehensive research import
- Toggle Single Two Pass Screening mode in Settings
- Turn on Automatic Training of the Screening Model in Settings, which will activate once 50 records are screened
- Apply a bulk action of including studies above assigned threshold and excluding studies below threshold
- Configure tag hierarchy with General PICO template to encompass overarching, scoping questions
- Turn on Abstract or Full Text Smart Tag Recommendations
- Either manually accept/reject recommendations or apply a bulk action of accepting all tag recommendations to create preliminary, non-quality-controlled outputs
- Use a Critical Appraisal system to assess Risk of Bias
- Download Exports/Spreadsheets in Study Inspector
- Assess and present evidence in Synthesis outputs
- Depending on your project, you may wish to use Dashboard or Manuscript
View an example of a Scoping Review in Nested Knowledge.
Narrative Review
For researchers aiming to conduct an extensive description and interpretation of previously published writing on a chosen topic. Narrative reviews provide a flexible and rigorous approach to analysing and interpreting the literature in a written format.
Suggested Nest Setup:
- Enter broad PICO terms and build out initial search query in Search Exploration
- Toggle Dual Standard Screening mode in Settings
- Turn on Robot Screener in Settings, once 50 records are screened
- Auto-adjudicate Robot Screener agreements and adjudicate disagreements
- Configure tag hierarchy with General PICO template to encompass overarching, scoping questions
- Turn on Abstract or Full Text Smart Tag Recommendations
- Either manually accept/reject recommendations or apply a bulk action of accepting all tag recommendations to create preliminary, non-quality-controlled outputs
- Use a Critical Appraisal system to assess Risk of Bias
- Download Exports/Spreadsheets in Study Inspector
- Assess and present evidence in Synthesis outputs
- Depending on your project, you may wish to use Dashboard or Manuscript
View an example of a Narrative Review in Nested Knowledge.
Gap Analysis
Nested Knowledge supports researchers in identifying gaps in existing literature through comprehensive gap analyses. By systematically reviewing the current state of knowledge, researchers can pinpoint areas where further research is needed, contributing to the advancement of their respective fields.
Suggested Nest Setup:
- Enter broad PICO terms and build out initial search query in Search Exploration
- Toggle Standard, Single Screening mode in Settings
- Turn on Automatic Training of the Screening model in Settings, which will activate once 50 records are screened
- Apply a bulk action including records above assigned threshold and excluding below assigned threshold
- Configure Tag hierarchy with high specificity to identify gaps
- Turn on Abstract or Full Text Smart Tag Recommendations
- Either manually accept/reject recommendations or apply a bulk action of accepting all tag recommendations to create preliminary, non-quality-controlled outputs
- If necessary, use a Critical Appraisal system to assess Risk of Bias
- Download Exports/Spreadsheets in Study Inspector
- Assess and present evidence in Synthesis outputs
View an example of a Gap Analysis in Nested Knowledge.
Now that we've defined each review type, take a look at the following visual to decide what review type is best for your project and explore the features tailored to each methodology in Nested Knowledge.